Internet Protocols (IP) and IP-based Telecommunication Networks Research

The Internet Protocol (IP) is a core technology not only for the Internet itself but also for modern telecommunication networks. The Internet and the IP-based telecommunications networks, along with other access technologies such as Wifi, form the mobile Internet that most of us rely on every day.
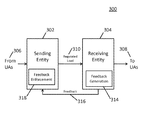
In its early days, the deployment of IP-based telecommunication services faced several key challenges in Internet signaling that hindered its wide adoption. Internet signaling is a process used to establish a multimedia communication session so that people can exchange data, voice, or video with each other on the Internet. However, when there are too many people using the service at the same time, the server experiences congestion and its performance collapses, i.e., becoming unresponsive to any existing or new user. The signaling could also malfunction if it was traversing both the traditional IPv4 and the newer IPv6 Internet.
Charles conducted in-depth research and co-invented a series of algorithms that solve the signaling server congestion collapse and IPv6 signaling transportation problem. The work helps ensure that IP-based telecommunications networks can meet the scalability and reliability requirements for a huge number of users in any condition. The results from this effort, in collaboration with researchers from Columbia University, NTT, Bell Labs, AT&T, Samsung, and Sonus Networks, have been granted several United States patents and become Internet Standards.
Granted US patents


Internet Standardization